Accounting
Done For You
Our financial accounting, Controller, and CFO services are tailored to bolster and improve the financial health of your business.

Financial Accounting, Analysis, and Management Services Delivered By Licensed Practitioners!
Financial Accounting
We use a tactical approach with a focus on historical data to maintain growth in the organization.
Controller Services
We use a tactical approach grounded in historical data analysis, enabling growth within the organization.
CFO Services
We use a financial approach with a forward-looking focus to foster organizational growth and development.
Financial Accounting



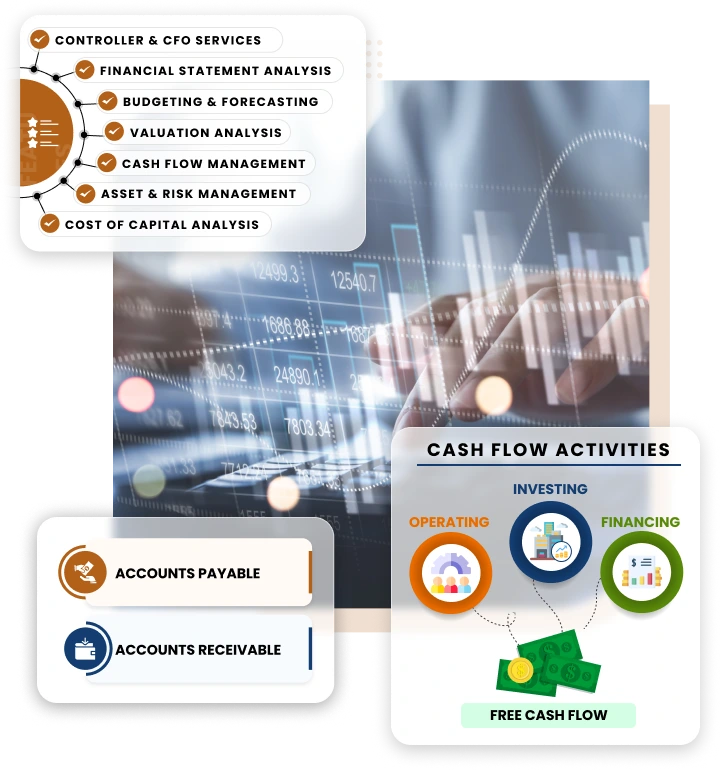
Central to our services is the preparation of core financial statements – the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement. Alongside these, we manage accounts payable and accounts receivable. Together, these services form a comprehensive financial accounting solution, designed to provide a clear and accurate financial picture, while supporting the day-to-day financial operations.
Financial Statements
Based on accurate and up-to-date bookkeeping data, we prepare the three core financial documents that provide an overview of a business’s financial performance and position at a specific point in time. The primary statements prepared are:
- Balance Sheet: Shows the company's assets, liabilities, and shareholders' equity, giving a snapshot of its financial position.
- Income Statement (Profit and Loss Statement): Details the company's revenues and expenses over a period, highlighting its profitability.
- Cash Flow Statement: Tracks the flow of cash in and out of the business, showing how well the company manages its cash for operational needs, financing activities, and investments.
These statements are essential for decision-making by management, investors, lenders, and other stakeholders, providing transparency and insights into the company’s financial health.
Accounts Payable
This function deals with managing the money a business owes to its suppliers or creditors. It involves receiving, processing, and verifying invoices; managing payment terms; and processing payments to suppliers. Efficient AP management helps maintain good supplier relationships, manage cash flows effectively, and avoid late payment fees or penalties.
Accounts Payable Features
- Automatic 2-way sync with QuickBooks Online and Xero
- Manage bills from a centralized inbox
- Easily enter bills
- Connect with +4M vendors
- Access unlimited document storage
- Pay by ACH, virtual card, credit card, and more
- Set custom approval policies
- Set custom user roles
Accounts Receivable
Conversely, accounts receivable focuses on the money owed to the business by its customers. This process includes invoicing, tracking customer payments, and managing collections for outstanding invoices. Effective AR management ensures that the business collects its revenues in a timely manner, which is crucial for maintaining healthy cash flow and overall financial stability.
Accounts Receivable Features
- Automatic 2-way sync with QuickBooks Online and Xero
- Create professional, custom invoices
- Send single or recurring invoices
- Track payment status with ease
- Set up automated payment reminders
- Get paid by ACH and credit card
- Set auto-charge and auto-pay


Our Controller services including financial statement analysis and accounting asset and risk management offer a dual approach to fortify your business’s financial integrity and strategic planning. This comprehensive service package ensures not only the meticulous analysis of your financial statements but also the proactive management of your assets and risks, paving the way for sustainable growth and financial resilience.
Controller Services

Financial Statement Analysis
Financial statement analysis is a methodical approach to evaluating and understanding a company’s financial health and performance using data derived from its financial statements. This analysis is essential for stakeholders like management, investors, lenders, and analysts to make informed decisions regarding the company’s operations, investments, and potential for future growth.
Key Components of Financial Statement Analysis
- Horizontal Analysis: This involves comparing financial data over a series of periods. It helps in identifying trends, such as increases or decreases in revenue or expenses, and assessing how the company is performing over time.
- Vertical Analysis: Also known as common-size analysis, this approach involves expressing each item in the financial statement as a percentage of a base figure. For example, in an income statement, each item may be represented as a percentage of total sales. This analysis helps in understanding the relative significance of each item and its impact on the company’s financial situation.
- Ratio Analysis: This involves calculating various financial ratios, such as profitability ratios, liquidity ratios, leverage ratios, and efficiency ratios. These ratios provide insights into different aspects of the company's financial health, like its ability to pay debts, efficiently use resources, and generate profits.
- Comparative Analysis: This compares a company's financial ratios and other metrics with those of other companies in the same industry, or with industry averages. This benchmarking helps in understanding the company's competitive position.
- Cash Flow Analysis: This assesses the company’s ability to generate cash and cash equivalents, focusing on its cash flow from operating, investing, and financing activities.
Financial statement analysis is an integral part of financial management, offering a comprehensive view of a company’s financial performance and assisting various stakeholders in making well-informed economic decisions.
Asset & Risk Management
Accounting asset and risk management refers to the systematic approach of managing and safeguarding a company’s financial resources, focusing on optimizing asset utilization and mitigating financial risks. This multifaceted discipline combines aspects of accounting, finance, and risk management to ensure that a company’s assets are efficiently utilized and protected against potential financial uncertainties.
Key Components of Accounting Asset & Risk Management
- Asset Management: In accounting, this involves overseeing and handling the company's assets to ensure they are accounted for, properly valued, and utilized effectively. It includes tracking assets' acquisition, depreciation, and disposal, managing inventory, and overseeing investments. Effective asset management ensures that the company's resources contribute positively to its financial performance and strategic objectives.
- Risk Management: This aspect focuses on identifying, assessing, and addressing potential financial risks that could impact the organization. It encompasses a wide range of risks, including credit risk, liquidity risk, operational risk, market risk, and regulatory risks. Risk management involves developing strategies and controls to mitigate these risks, such as diversifying investments, establishing contingency plans, and maintaining insurance policies.
- Financial Reporting and Compliance: Ensuring accurate financial reporting and compliance with accounting standards and regulations is a crucial part of asset and risk management. It involves implementing internal controls, policies, and procedures that promote transparency, accuracy, and integrity in financial reporting.
- Strategic Decision-Making: Asset and risk management contribute to strategic decision-making by providing valuable insights into financial performance and risk exposure. This information helps management in making informed decisions about investments, resource allocation, and business strategies.
- Liquidity Management: Managing the liquidity of the company is an integral part of this process. It involves ensuring that the organization has enough cash flow to meet its short-term liabilities and commitments without compromising long-term financial stability.
- Internal Controls and Audits: Establishing robust internal controls and conducting regular audits are essential for preventing errors, fraud, and financial misstatements. They play a significant role in protecting assets and ensuring the reliability of financial information.
Accounting asset and risk management is vital for maintaining the financial health of an organization. It helps in optimizing the use of assets for generating revenue and growth while protecting the company from financial uncertainties and compliance issues. By effectively managing assets and risks, organizations can achieve financial stability, maintain investor confidence, and ensure long-term sustainability.
CFO Services



Our CFO services are tailored to enhance an organization’s strategic decision-making processes. With a suite of integrated tools that include budgeting, financial forecasting, cost of capital analysis, and business valuation analysis, our CFO role is not just about managing finances but also about providing strategic guidance to propel business forward.
Budgeting
Budgeting is a critical process for managing an organization’s financial resources. It involves creating a detailed plan that outlines expected revenues and expenditures over a specific period, typically a year. This plan serves as a roadmap for the organization to allocate resources, prioritize expenditures, and achieve its financial goals.
Key Aspects of Budgeting
- Revenue Estimation: This is the first step where projected income sources are identified and quantified. It involves estimating how much revenue the organization expects to receive from various sources like sales, services, investments, or grants.
- Expense Forecasting: In this step, all expected costs are itemized. This includes fixed costs like rent and salaries, and variable costs such as materials, utilities, and marketing expenses.
- Resource Allocation: Budgeting involves deciding how to allocate available financial resources among various departments, projects, or initiatives. This allocation is based on the organization's priorities and strategic goals.
- Cash Flow Management: Budgeting helps in anticipating cash flow needs, ensuring that the organization has sufficient funds to cover its liabilities and avoiding over- or under-spending.
- Performance Monitoring: Once the budget is set, it acts as a tool for monitoring financial performance. It provides a benchmark against which actual revenues and expenses can be compared to identify variances.
- Strategic Planning: Budgeting is not just about numbers; it's an integral part of strategic planning. It helps organizations plan for future growth and make informed decisions about long-term investments.
- Financial Goals and Objectives Setting: A budget sets financial targets for the organization, such as profit margins, cost reduction goals, or investment in new projects.
Budgeting guides organizations in their financial planning and management. It’s a dynamic tool that not only sets financial expectations but also facilitates overall strategic planning, control, and effective decision-making.
Financial Forecasting
Financial forecasting is used to predict the future financial state of an organization based on historical data, current market trends, and informed assumptions. This process plays a crucial role in strategic planning and decision-making, providing businesses with a forward-looking perspective that aids in navigating future financial challenges and opportunities.
Key Aspects of Financial Forecasting
- Revenue Projection: This involves estimating future sales and income, considering factors like market trends, historical sales data, industry analysis, and economic conditions. Revenue projection helps in setting realistic goals for business growth and performance.
- Expense Estimation: Forecasting future costs is equally important. This includes predicting operating expenses, cost of goods sold, salaries, and other overheads. Understanding potential expenses allows for better budget management and cost control.
- Cash Flow Analysis: Forecasting cash flow involves predicting the inflow and outflow of cash. This is critical for assessing the liquidity of the business, ensuring it has enough cash to meet its obligations, and planning for investment or expansion.
- Profit and Loss Forecasting: This combines revenue and expense forecasts to predict future profitability. It helps businesses anticipate periods of high or low profitability and plan accordingly.
- Capital Budgeting: Financial forecasting is essential in capital budgeting decisions, where businesses determine how to allocate their capital resources to maximize returns on investments.
- Scenario Analysis: It often involves creating multiple scenarios (like best-case, worst-case, and most-likely scenarios) to understand the potential impacts of different business conditions or decisions.
Financial forecasting enables businesses to plan for the future with greater clarity and confidence. By providing a projected financial roadmap, it helps businesses navigate uncertainty, manage risks, and capitalize on potential opportunities.
Cost of Capital Analysis
Cost of Capital Analysis is a crucial financial assessment used to determine the total cost of a company’s funds, both debt and equity. It serves as a critical financial metric in strategic planning and financial management. It helps companies balance their growth and profitability objectives with the risks and costs associated with their capital structure. By understanding the cost of their capital, businesses can make more informed decisions about funding projects, financing their operations, and creating value for shareholders.
Cost of Capital Components
- Cost of Debt: This is the effective rate a company pays on its borrowed funds, such as loans and bonds. The cost of debt is often easier to calculate as it is based on the observable interest rates the company is paying on its debts. However, it's important to consider the tax implications since interest expenses are generally tax-deductible, reducing the actual cost of debt.
- Cost of Equity: This refers to the return a company requires to decide if an investment meets capital return requirements. It's often calculated using models like the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), which considers the risk-free rate of return, the equity beta (risk factor relative to the market), and the market risk premium.
Cost of Capital Analysis provides a comprehensive view of the expense of a company’s financial resources. It plays a vital role in guiding investment decisions, evaluating company performance, and ensuring that a company’s financial strategies align with its overall business objectives.
Business Valuation Analysis
Business Valuation Analysis is a critical financial process that determines the economic value of a company or business unit. This analysis is essential for a variety of purposes, including mergers and acquisitions, sale of the business, estate and tax planning, and strategic planning. It involves using a set of procedures and valuation methods to assess the worth of a business in monetary terms.
Business Valuation Methods
- Income Approach: Estimates future cash flows and discounts them to present value.
- Asset-Based Approach: Focuses on the value of the company's assets minus its liabilities.
- Market Approach: Compares the business to similar companies that have been sold recently.
Business Valuation Analysis is not just about determining a price tag for a business; it’s about understanding what drives value in the company. This information is vital for business owners, investors, and potential buyers to make informed decisions. For instance, in mergers and acquisitions, accurate valuation ensures that all parties involved receive fair value. For business owners, understanding the value of their business helps in strategic planning and decision-making, especially in terms of investments, growth strategies, and potential exits.